This tutorial will teach you a few simple tricks to delete multiple empty rows in Excel safely without losing a single bit of information.
Blank rows in Excel is a problem we all face once in a while, especially when combining data from different sources or importing information from somewhere else. Empty lines can cause a lot of havoc to your worksheets on different levels and deleting them manually can be a time-consuming and error-prone process. In this article, you will learn a few simple and reliable methods to remove blanks in your worksheets.
How NOT to remove blank lines in Excel
There are a few different ways to delete empty lines in Excel, but surprisingly many online resources stick with the most dangerous one, namely Find & Select > Go To Special > Blanks.
What's wrong about this technique? It selects all blanks in a range, and consequently you will end up deleting all rows that contain as much as a single blank cell.
The below image shows the original table on the left and the resulting table on the right. And in the resulting table, all incomplete rows ae gone, even row 10 where only the date in column D was missing:
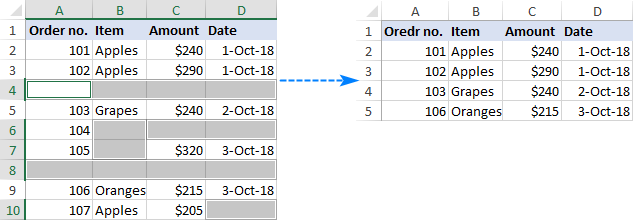
The bottom line: if you don't want to mess up your data, never delete empty rows by selecting blank cells. Instead, use one of the more considered approaches discussed below.
How to remove blank rows in Excel with VBA
Excel VBA can fix a lot of things, including multiple empty rows. The best thing about this approach is that it does not require any programming skills. Simply, grab one of the below codes and run it in your Excel (the instructions are here).
Macro 1. Delete blank lines in a selected range
This VBA code silently deletes all blank rows in a selected range, without showing any message or dialog box to the user.
Unlike the previous technique, the macro deletes a line if the entire row is empty. It relies on the worksheet function CountA to get the number of non-empty cells in each line, and then deletes rows with the zero count.
To give the user an opportunity to select the target range after running the macro, use this code:
Upon running, the macro shows the following input box, you select the target range, and click OK:
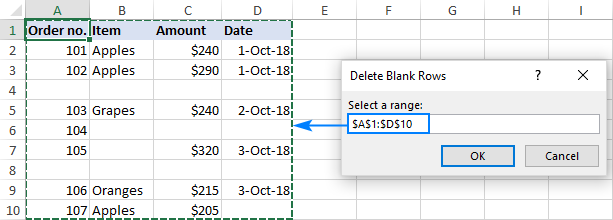
In a moment, all empty lines in the selected range will be eliminated and the remaining ones will shift up:

Macro 2. Delete all blank rows in Excel
To remove all blank rows on the active sheet, determine the last row of the used range (i.e. the row containing the last cell with data), and then go upwards deleting the lines for which CountA returns zero:
Macro 3. Delete row if cell is blank
With this macro, you can delete an entire row if a cell in the specified column is blank.
The following code checks column A for blanks. To delete rows based on another column, replace "A" with an appropriate letter.
As a matter of fact, the macro uses the Go To Special > Blanks feature, and you can achieve the same result by performing these steps manually.
Note. The macro deletes blank rows in the entire sheet, so please be very careful when using it. As a precaution, it may be wise to back up the worksheet before running this macro.
How to remove blank lines in Excel with VBA
To delete empty rows in Excel using a macro, you can either insert the VBA code into your own workbook or run a macro from our sample workbook.
Add a macro to your workbook
To insert a macro in your workbook, perform these steps:
- Open the worksheet where you want to delete blank rows.
- Press Alt + F11 to open the Visual Basic Editor.
- On the left pane, right-click ThisWorkbook, and then click Insert > Module.
- Paste the code in the Code window.
- Press F5 to run the macro.
For the detailed step-by-step instructions, please see How to insert and use VBA in Excel.
Run a macro from our sample workbook
Download our sample workbook with Macros to Delete Blank Rows and run one of the following macros from there:
DeleteBlankRows - removes empty rows in the currently selected range.
RemoveBlankLines - deletes blank rows and shifts up in a range that you select after running the macro.
DeleteAllEmptyRows - deletes all empty lines on the active sheet.
DeleteRowIfCellBlank - deletes a row if a cell in a specific column is blank.
To run the macro in your Excel, do the following:
- Open the downloaded workbook and enable the macros if prompted.
- Open your own workbook and navigate to the worksheet of interest.
- In your worksheet, press Alt + F8, select the macro, and click Run.
Formula to delete blank rows in Excel
In case you'd like to see what you are deleting, use the following formula to identify empty lines:
=IF(COUNTA(A2:D2)=0, "Blank", "Not blank")
Where A2 is the first and D2 is the last used cell of the first data row.
Enter this formula in E2 or any other blank column in row 2, and drag the fill handle to copy the formula down.
As the result, you will have "Blank" in empty rows and "Not blank" in the rows that contain at least one cell with data:

The formula's logic is obvious: you count non-empty cells with the COUNTA function and use the IF statement to return "Blank" for zero count, "Not Blank" otherwise.
In fact, you can do nicely without IF:
=COUNTA(A2:D2)=0
In this case, the formula will return TRUE for blank lines and FALSE for non-blank lines.
With the formula in place, carry out these steps to delete empty lines:
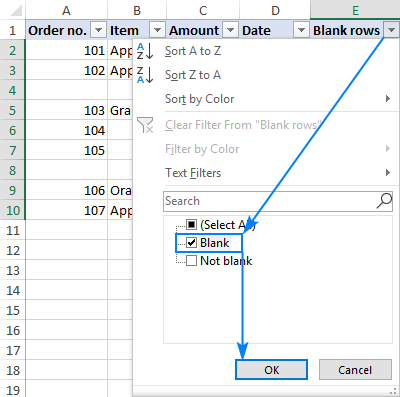
- Select any cell in the header row and click Sort & Filter > Filter on the Home tab, in the Formats This will add the filtering drop-down arrows to all header cells.
- Click the arrow in the formula column header, uncheck (Select All), select Blank and click OK:
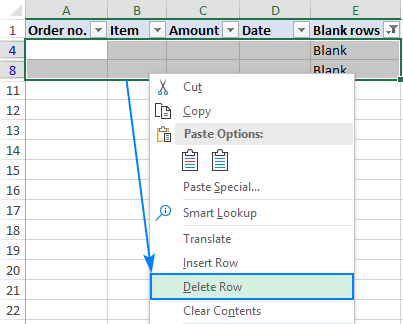
- Select all the filtered rows. For this, click on the first cell of the first filtered row and press Ctrl + Shift + End to extend the selection to the last cell of the last filtered row.
- Right-click the selection, choose Delete row from the context menu, and then confirm that you really want to delete entire rows:
- Remove the filter by pressing Ctrl + Shift + L. Or click Home tab > Sort & Filter > Filter.
- Delete the column with the formula since you do not need it any longer.
That's it! As the result, we have a clean table with no blank lines, but all the information preserved:

Tip. Instead of deleting empty lines, you can copy non-empty rows to somewhere else. To have it done, filter "Not blank" rows, select them and press Ctrl + C to copy. Then switch to another sheet, select the upper-left cell of the destination range and press Ctrl + V to paste.
How to remove empty lines in Excel with Power Query
In Excel 2016 and Excel 2019, there is one more way to delete empty rows - by using the Power Query feature. In Excel 2010 and Excel 2013, it can be downloaded as an add-in.
Important note! This method works with the following caveat: Power Query converts the source data into an Excel table and changes the formatting such as fill color, borders and some number formats. If the formatting of your original data is important to you, then you'd better choose some other way to remove blank rows in Excel.
- Select the range where you want to delete empty lines.
- Go to the Data tab > Get & Transform group and click From Table/Range. This will load your table to the Power Query Editor.

- On the Home tab of the Power Query Editor, click Remove Rows > Remove Blank Rows.
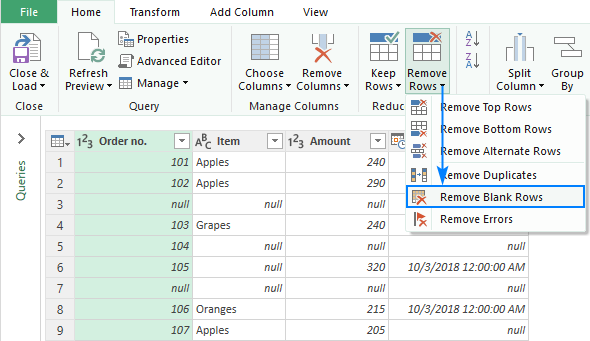
- Click the Close & Load This will load the resulting table to a new worksheet and close the Query Editor.
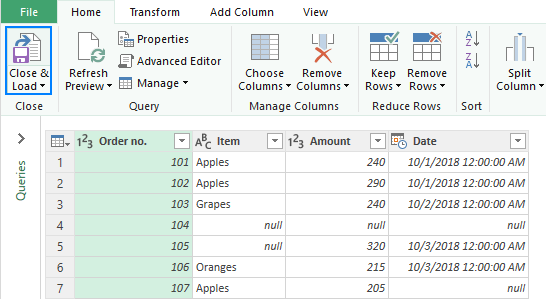
In the result of these manipulations, I got the following table without empty lines, but with a couple of nasty changes - the currency format is lost and the dates are displayed in the default format instead of the custom one:

If you are curious to learn other applications of this powerful feature, you can find more practical examples in this tutorial: Using Power Query in Excel.
How to delete rows if cell in a certain column is blank
In the beginning of this tutorial, we warned you against removing empty lines by selecting blanks. However, this method comes in handy if you want to delete rows based on blanks in a specific column.
As an example, let's remove all the rows where a cell in column A is empty:
- Select the key column, column A in our case.
- On the Home tab, click Find & Select > Go To Special. Or press F5 and click the Special… button.

- In the Go To Special dialog, select Blanks and click OK. This will select blank cells in the used range in column A.

- Right-click on any selected cell and choose Delete… from the context menu.
- In the Delete dialog box, choose Entire row and click OK.

Done! The rows that do not have a value in column A are no longer there:

The same result can be achieved by filtering blanks in the key column.
How to remove extra lines below data
Sometimes, the rows that look completely blank may actually contain some formats or non-printable characters. To check if the last cell with data is really the last used cell in your worksheet, press Ctrl + End. If this has taken you to a visually empty row below your data, in terms of Excel, that row is not blank. To remove such rows, do the following:
- Click the header of the first blank row below your data to select it.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + End. This will select all the lines that contain anything including formats, spaces and non-printing characters.
- Right-click the selection and choose Delete… > Entire row.

If you have a relatively small data set, you may want to get rid of all blank lines below your data, e.g. to make scrolling easier. Although, there is no way to delete unused rows in Excel, there is nothing that would prevent you from hiding them. Here's how:
- Select the row below the last row with data by clicking its header.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Down arrow to extend the selection to the last row on the sheet.
- Press Ctrl + 9 to hide the selected rows. Or right-click the selection, and then click Hide.

To unhide the rows, press Ctrl + A to select the entire sheet, and then press Ctrl + Shift + 9 to make all the lines visible again.
In a similar fashion, you can hide unused blank columns to the right of your data. For the detailed steps, please see Hide unused rows in Excel so that only working area is visible.
Fastest way to remove empty rows in Excel
When reading the previous examples, didn't it feel like we were using a sledgehammer to crack a nut? Here, at Ablebits, we prefer not to make things more complex than they need to be. So, we took a step further and created a two-click route to delete empty rows in Excel.
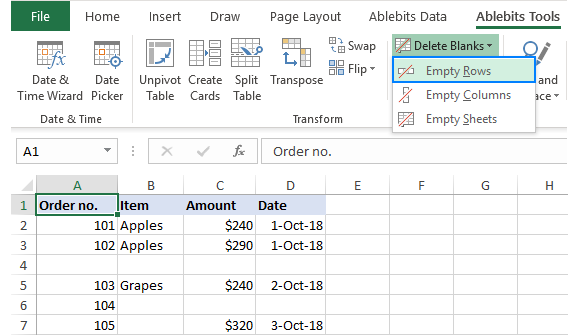
With the Ultimate Suite added to your ribbon, here's how you can delete all empty rows in a worksheet:
- On the Ablebits Tools tab, in the Transform group, click Delete Blanks > Empty Rows:
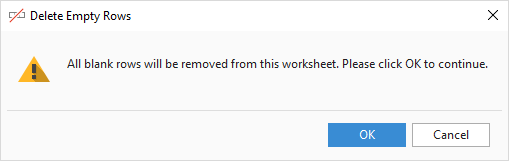
- The add-in will inform you that all empty rows are going to be removed from the active worksheet and ask to confirm. Click OK, and in a moment, all blank rows will be eliminated.
As shown in the screenshot below, we have only removed absolutely blank lines that do not have a single cell with data:

To find out more awesome features included with our Ultimate Suite for Excel, you are welcome to download a trial version.
I thank you for reading and hope to see you on our blog next week!
 by
by
26 comments
thanks for this. very helpful