The tutorial shows how to perform spell check in Excel manually, with VBA code, and by using a special tool. You will learn how to check spelling in individual cells and ranges, active worksheet and the entire workbook.
Although Microsoft Excel is not a word processing program, it does have a few features to work with text, including the spell-checking facility. However, spell check in Excel is not exactly the same as in Word. It does not offer advanced capabilities like grammar checking, nor does it underline the misspelled words as you type. But still Excel provides the basic spell checking functionality and this tutorial will teach you how to get most of it.
How to do spell check in Excel
No matter which version you are using, Excel 2016, Excel 2013, Excel 2010 or lower, there are 2 ways to spell check in Excel: a ribbon button and a keyboard shortcut.
Simply, select the first cell or the cell from which you'd like to start checking, and do one of the following:
- Press the F7 key on your keyboard.
- Click the Spelling button on the Review tab, in the Proofing group.
This will perform a spelling check on the active worksheet:
When a mistake is found, the Spelling dialog window shows up:
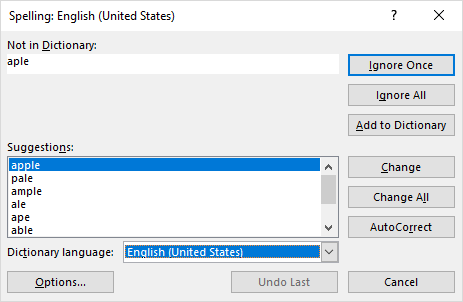
To correct a mistake, choose an appropriate opting under Suggestions, and click the Change button. The misspelt word will be replaced with the selected one and the next mistake will be brought to your attention.
If the "mistake" is not really a mistake, pick one of the following options:
- To ignore the current mistake, click Ignore Once.
- To ignore all the mistakes same as the current one, click Ignore All.
- To add the current word to dictionary, click Add to Dictionary. This will ensure that the same word won't be treated as a mistake when you do a spell check next time.
- To replace all the mistakes same as the current one with the selected suggestion, click Change All.
- To let Excel correct the mistake as it sees fit, click AutoCorrect.
- To set another proofing language, select it from the Dictionary language drop box.
- To view or change the spell check settings, click the Options… button.
- To stop the correction process and close the dialog, click the Cancel button.
When the spell check is complete, Excel will show you the corresponding message:
Spell check individual cells and ranges
Depending on your selection, Excel Spell check processes different areas of the worksheet:
By selecting a single cell, you tell Excel to perform spell check on the active sheet, including text in the page header, footer, comments, and graphics. The selected cell is the starting point:
- If you select the first cell (A1), the entire sheet is checked.
- If you select some other cell, Excel will start spell checking from that cell onward till the end of the worksheet. When the last cell is checked, you will be prompted to continue checking at the beginning of the sheet.
To spell check one particular cell, double-click that cell to enter the edit mode, and then initiate spell check.
To check spelling in a range of cells, select that range and then run the spell-checker.
To check only part of the cell contents, click the cell and select the text to check in the formula bar, or double click the cell and select the text in the cell.
How to check spelling in multiple sheets
To check several worksheets for spelling mistakes at a time, do the following:
- Select the sheet tabs you wish to check. For this, press and hold the Ctrl key while clicking the tabs.
- Press the spell check shortcut (F7) or click the Spelling button on the Review tab.
Excel will check spelling mistakes in all the selected worksheets:
When the spell check is completed, right click the selected tabs and click Ungroup sheets.
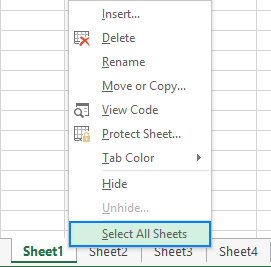
How to spell check the entire workbook
To check spelling in all the sheets of the current workbook, right click on any sheet tab and pick Select all Sheets from the context menu. With all the sheets selected, press F7 or click the Spelling button on the ribbon. Yep, it's that easy!
How to spell check text in formulas
Normally, Excel does not check formula-driven text because a cell actually contains a formula, not a text value:
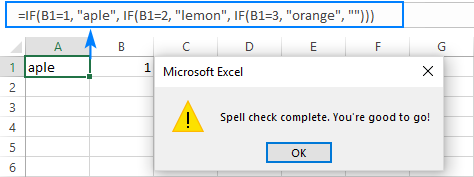
However, if you get in the edit mode and then run spell check, it will work:
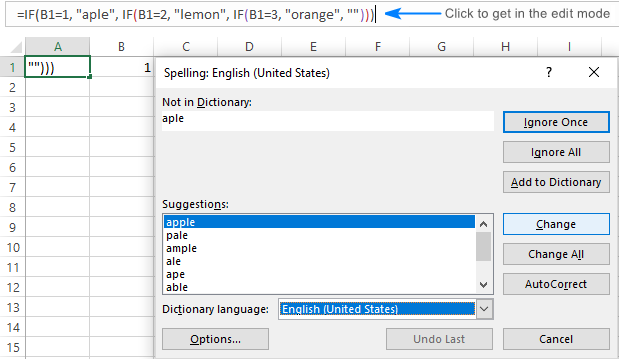
Of course, you will need to check each cell individually, which is not very good, but still this approach may help you eliminate spelling errors in big formulas, for example, in multi-level nested IF statements.
Spell check in Excel using a macro
If you like automating things, you can easily automate the process of finding wrongly spelled words in your worksheets.
Macro to do spell check in the active sheet
What can be simpler than a button click? Maybe, this line of code :)
Macro to spell check all sheets of the active workbook
You already know that to search for spelling mistakes in multiple sheets, you select the corresponding sheet tabs. But how do you check hidden sheets?
Depending on your target, use one of the following macros.
To check all visible sheets:
To check all sheets in the active workbook, visible and hidden:
Highlight misspelled words in Excel
This macro allows you to find the misspelled words simply by viewing the sheet. It highlights the cells containing one or more spelling mistakes in red. To use another background color, change the RGB code in this line: cell.Interior.Color = RGB(255, 0, 0).
How to use spell checking macros
Download our sample workbook with Spell Check macros, and perform these steps:
- Open the downloaded workbook and enable the macros if prompted.
- Open your own workbook and switch to the worksheet you want to check.
- Press Alt + F8, select the macro, and click Run.
The sample workbook contains the following macros:
- SpellCheckActiveSheet - performs a spell check in the active worksheet.
- SpellCheckAllVisibleSheets - checks all visible sheets in the active workbook.
- SpellCheckAllSheets - checks visible and invisible sheets in the active workbook.
- HighlightMispelledCells - changes the background color of cells that contain wrongly spelled words.
You can also add the macros to you own sheet by following these instructions: How to insert and run VBA code in Excel.
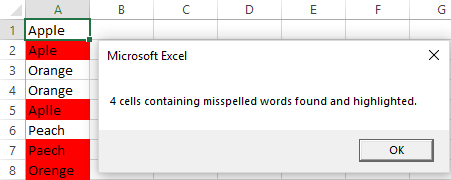
For example, to highlight all the cells with spelling errors in the current spreadsheet, run this macro:
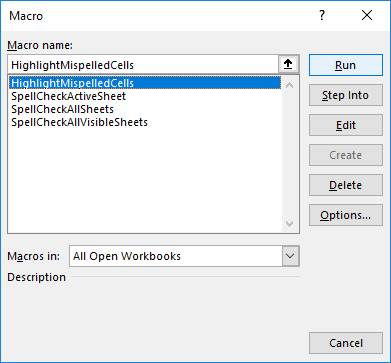
And get the following result:
Change the Excel spell check settings
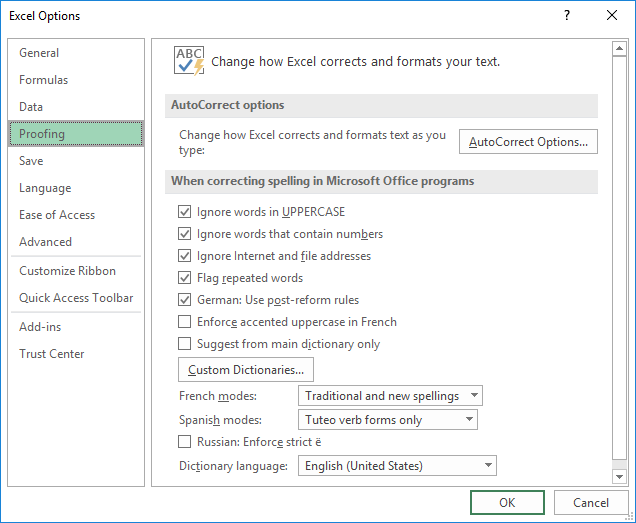
If you'd like to tweak the behavior of spell check in Excel, click File > Options > Proofing, and then check or uncheck the following options:
- Ignore words in uppercase
- Ignore words that contain numbers
- Ignore internet files and addresses
- Flag repeated words
All the options are self-explanatory, maybe except the language-specific ones (I can explain about enforcing strict ё in the Russian language if someone cares :)
The screenshot below shows the default settings:
Excel spell check not working
If spell check does not work properly in your worksheet, try these simple troubleshooting tips:
Spelling button is greyed out
Most likely your worksheet is protected. Excel spell check does not work in protected sheets, so you will have to unprotect your worksheet first.
You are in edit mode
When in edit mode, only the cell you are currently editing is checked for spelling errors. To check the whole worksheet, exit the edit mode, and then run spell check.
Text in formulas is not checked
Cells containing formulas are not checked. To spell check text in a formula, get in the edit mode.
Find typos and misprints with Fuzzy Duplicate Finder
In addition to the built-in Excel spell check functionality, the users of our Ultimate Suite can quickly find and fix typos by using a special tool that resides on the Ablebits Tools tab under Find and Replace:
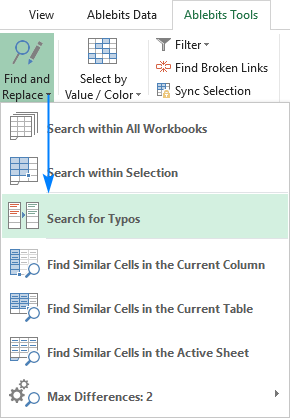
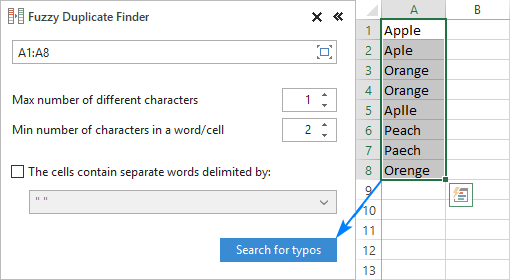
Clicking the Search for Typos button opens the Fuzzy Duplicate Finder pane on the left side of your Excel window. You are to select the range to check for typos and configure the settings for your search:
- Max number of different characters - limit the number of differences to look for.
- Min number of characters in a word/cell - exclude very short values from the search.
- The cells contain separate words delimited by - select this box if your cells may contain more than one word.
With the settings properly configured, click the Search for typos button.
The add-in starts searching for values that differ in 1 or more characters, as specified by you. Once the search is finished, you are presented with a list of the found fuzzy matches grouped in nodes like shown in the screenshot below.
Now, you are to set the correct value for each node. For this, expand the group, and click the check symbol in the Action column next to the right value:
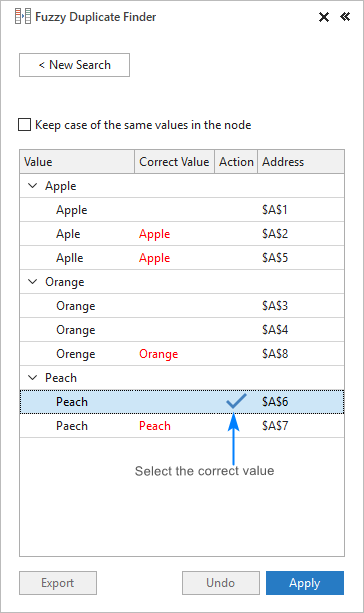
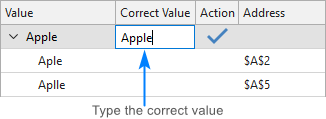
If the node doesn't contain the right word, click in the Correct Value box next to the root item, type the word, and press Enter.
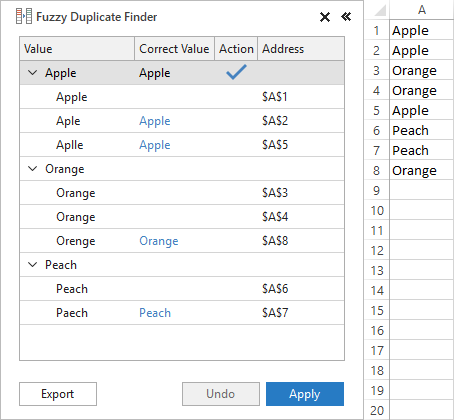
Upon assigning the correct values to all the nodes, click the Apply button, and all the typos in your worksheet will be fixed in one go:
That's how you perform spell check in Excel with Fuzzy Duplicate Finder. If you are curious to try this and 70+ more professional tools for Excel, you are welcome to download a trial version of our Ultimate Suite.
 by
by
3 comments
Hello:
I have a spreadsheet that Excel 365 review/spelling found a word that is not in the dictionary. I cannot find the work on the sheet. I have tried Ctrl-F in values, formulas, comments & notes, and it says is nothing to find. I don't see any hidden rows or columns either. How to I find where this word is?
Tks!
I found this code and it works for selecting and checking only cells that are unlocked. It doesn't highlight it, but you may be able to alter it using the above information to do what you want.
Sub SelectUnlockedCells_Spellcheck()
ActiveSheet.Unprotect Password:="****"
Dim WorkRange As Range
Dim FoundCells As Range
Dim Cell As Range
Set WorkRange = ActiveSheet.UsedRange
For Each Cell In WorkRange
If Cell.Locked = False Then
If FoundCells Is Nothing Then
Set FoundCells = Cell
Else
Set FoundCells = Union(FoundCells, Cell)
End If
End If
Next Cell
If FoundCells Is Nothing Then
MsgBox "All cells are locked."
Else
FoundCells.CheckSpelling CustomDictionary:="CUSTOM.DIC", _
IgnoreUppercase:=False, AlwaysSuggest:=True, SpellLang:=3081
End If
ActiveSheet.Protect Password:="****"
End Sub
Hi,
I have been trying to find a solution for some time, without success, to a problem I have with a spell check macro on a protected worksheet. What I am trying to achieve is a macro that will spell check only unlocked cells while highlighting the cell where an error is found.
The CheckSpelling method will check only the unlocked cells but will not highlight the cell where an error is found.
The Application.CommandBars("Tools").Controls("Spelling...").Execute method will highlight the cell where an error is found but checks ALL cells including unlocked.
I have posted this to my usual forum but nobody appears to have a solution.