The tutorial shows different ways to combine sheets in Excel depending on what result you are after – copy all data into a single sheet, merge two spreadsheets into one by the key column, or consolidate data from multiple worksheets.
Today we'll tackle a problem that many Excel users are struggling with daily – merging multiple Excel sheets into one without spending hours copying and pasting.
For a few sheets, manual copying may work, but with dozens of them mistakes are inevitable. In this situation, automated merging is a more reliable approach. The article covers the most common scenarios:
How to merge sheets in Excel using VBA
If you are comfortable with macros, you can combine multiple Excel sheets into one by using a VBA script. Below you'll find four sample codes for typical use cases.
Important note! All the macros below write their results to a sheet named Summary. Before running any of them, check whether your workbook already contains a sheet with that name. If it does, its content will be cleared and replaced by the macro's output. If you want to keep an existing Summary sheet, either rename it in your workbook or change the VBA code so it places the results into a worksheet with a different name.
Code 1. Combine all sheets in the active workbook
This macro copies the data from every spreadsheet in the active workbook and pastes it into the Summary sheet, stacking each sheet's data one below another. It keeps everything intact, including values, formulas, and the original formatting, so the result looks just like the source sheets, only combined in one place.
How this code works:
- Looks for a worksheet named Summary. If it doesn't exist, the macro creates it. If the Summary sheet already exists, the macro clears it, so the output always reflects the latest run.
- Loops through all worksheets except Summary.
- Copies each sheet's UsedRange to the next available row on the Summary sheet.
- Continues stacking rows until all sheets have been merged into a single list.
Code 2: Merge spreadsheets with a single header row
If all sheets have the same column headers, you can use this version. It copies the header row only once (from the first non-empty sheet) and then pulls in data rows from all other sheets.
Note. This code assumes that all worksheets have the same column headers in the same order. It copies columns as-is and doesn't match them by header names. If your sheets contain the same columns but in a different order, you can utilize the Combine Sheets tool to match and merge data by column headers.
How this code works:
- Assumes the column headers are in the first row of each sheet's UsedRange.
- Uses the headerCopied Boolean flag to track whether the header row has already been written to the Summary sheet.
- On the first non-empty sheet, the macro copies the entire UsedRange (header + data).
- For all later sheets, it copies everything except the first row.
Code 3. Combine spreadsheets with name labels
If you'd like to keep track of where each block of data came from, this version writes the sheet name as a label before the data from that sheet. The header row still appears only once, at the top of the Summary sheet.
How this code works:
- Before each sheet's data, the macro adds a bold label with the sheet name (for example, Sheet1:) in column A, so it's easy to see where each group begins.
- As in the previous example, this code copies the header row from the first non-empty sheet only.
Code 4. Combine only selected worksheets
This macro merges only the currently selected sheets (grouped tabs) into the Summary sheet. This is handy when you don't want to include data from every tab in the workbook.
How to use this macro:
- In your Excel workbook, select the spreadsheets you want to combine:
- Hold Ctrl and click individual tabs, or
- Use Shift + click to select a range of tabs.
- Run the CombineSelectedSheets macro.
- The macro copies the header row from the first selected sheet with data, then appends data rows from all selected sheets, skipping their headers.
How to add the macro to your workbook
You can add any of the above macros to your workbook in this way:
- Open the file where you want to merge spreadsheets.
- Press Alt + F11 to open the Visual Basic Editor.
- In the Project pane on the left, right-click your workbook and choose Insert > Module.
- Paste the code in the module window.
For the detailed instructions, see How to insert and run VBA code in Excel.
Download the workbook with the macros
If you prefer to start from a ready-made file, you can download a sample workbook that already contains all the macros described in this tutorial:
- CombineSheets – copies data from all sheets in the active workbook.
- CombineSheetsWithSingleHeaderRow – joins all spreadsheets but adds a single header row.
- CombineSheetsWithLabels – inserts sheet name labels before each data block.
- CombineSelectedSheets – combines only the selected sheets in the active workbook.
To run the macros from the sample file in your own workbook, do this:
- Open the downloaded file and enable the macros if prompted.
- Open your own workbook that contains the sheets you want to combine.
- In your workbook, press Alt + F8, select the desired macro, and click Run.
How to combine Excel spreadsheets with Ultimate Suite
Microsoft Excel has many nice features for various tasks, but it doesn't provide a way to pull data from different sheets together into one place. This can be done using either a VBA macro or merge and combine tools included with our
Ultimate Suite for Excel.
Combine multiple worksheets into one with Copy Sheets
Supposing you have a few spreadsheets that contain information about different products, and you need to merge the content of these sheets into one worksheet, like this:
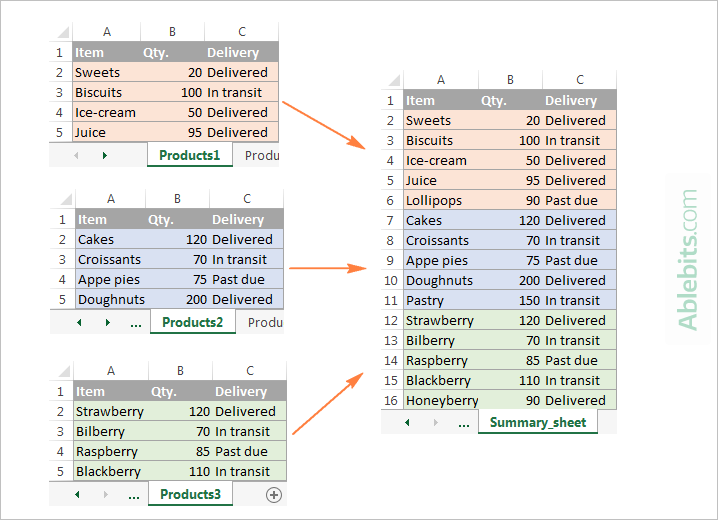
With the Copy Sheets added to your ribbon, the 3 simple steps is all it takes to merge the selected sheets into one.
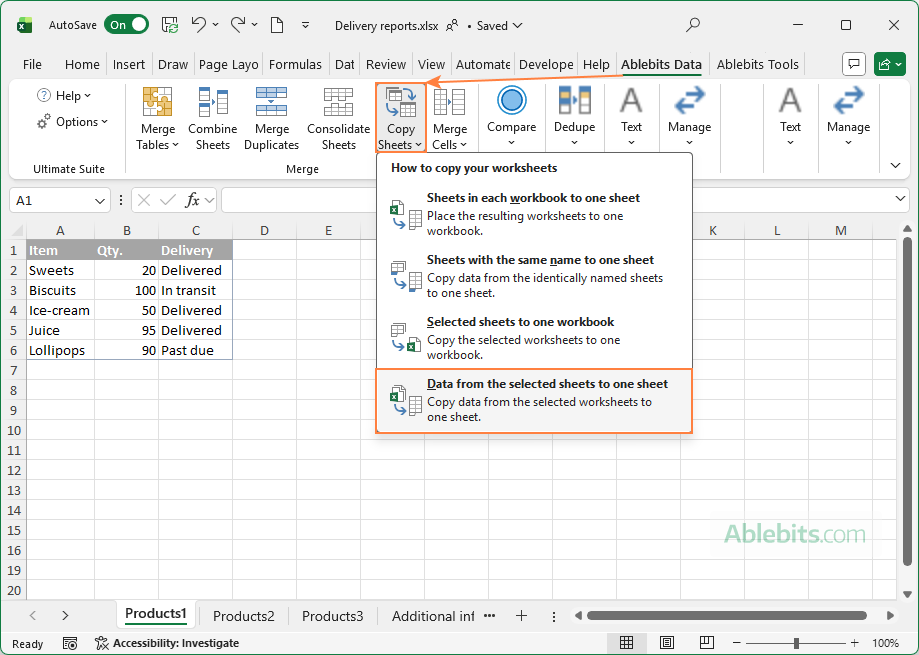
Step 1. Start the Copy Sheets Wizard
On the Excel ribbon, go to the Ablebits tab, click Copy Sheets, and choose one of the following options:
- Copy all sheets in each workbook into one sheet.
- Merge the identically named sheets.
- Copy the selected sheets to one workbook.
- Combine data from the selected sheets into one sheet.
If you aim to copy data from several worksheets into one, pick the last option:
Step 2. Select worksheets to merge
The Copy Sheets wizard shows a list of all tabs from all open workbooks. Simply select the ones you want to merge and click Next.
For cases where you only want part of a sheet, click the Collapse Dialog icon and highlight the range you'd like to include.
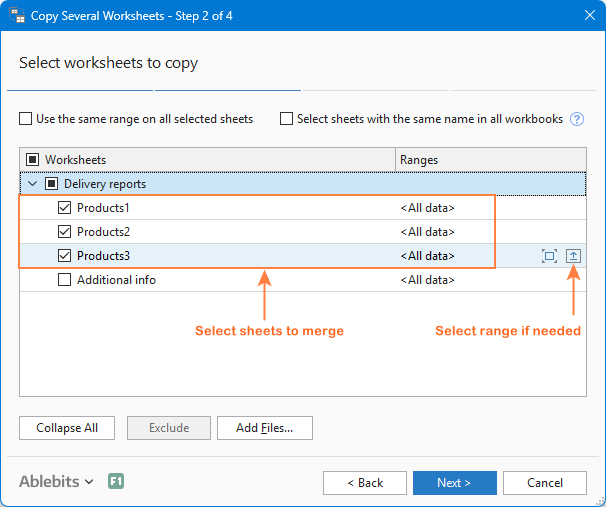
Tip. If the worksheets you want to merge are in a workbook that isn't open, click Add files… and browse for the workbook you want to pull data from.
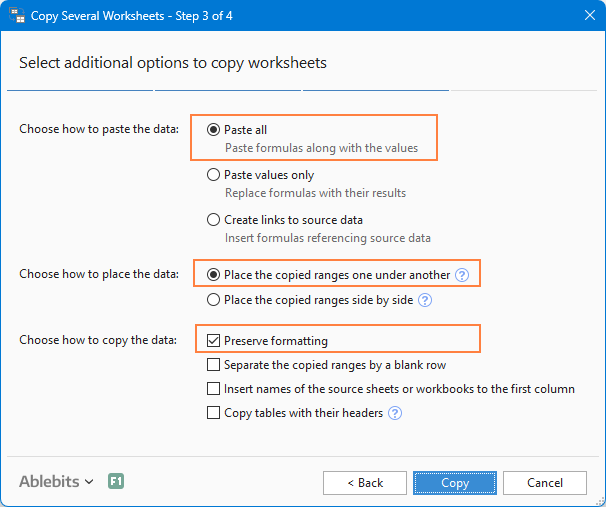
Step 3. Choose how to merge sheets
In the final step, you can choose a few additional settings to make sure the worksheets are combined exactly the way you need.
How to paste the data:
- Paste all - copy everything, including values and formulas. This is the most common choice.
- Paste values only - copy the results of formulas but not the formulas themselves. Choose this when you want a static summary.
- Create links to source data - insert formulas that reference the original cells. Pick this option if you want the combined sheet to update automatically when the source sheets change.
How to arrange the data:
- Place copied ranges one under another - stack the copied ranges vertically.
- Place copied ranges side by side - stack the copied ranges horizontally.
How to copy the data:
- Preserve formatting - self-explanatory and very convenient.
- Separate the copied ranges by a blank row - insert an empty row between the blocks of data copied from different sheets.
- Copy tables with their headers - include table headers in the final sheet.
The screenshot below shows the default settings that work fine in most cases:
Click the Copy button, and you will have the information from different sheets merged into one like shown in the beginning of this example.
Apart from the Copy Sheets add-in, the Ultimate Suite for Excel provides a few more merging tools to handle more specific scenarios.
Merge Excel sheets with a different order of columns
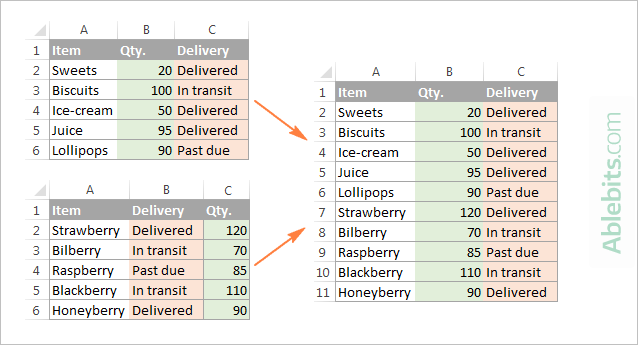
When your worksheets come from different users, the columns often appear in a different order. What do you do in that case: copy everything manually or rearrange each sheet first? Neither! Let the Combine Sheets wizard handle it for you:
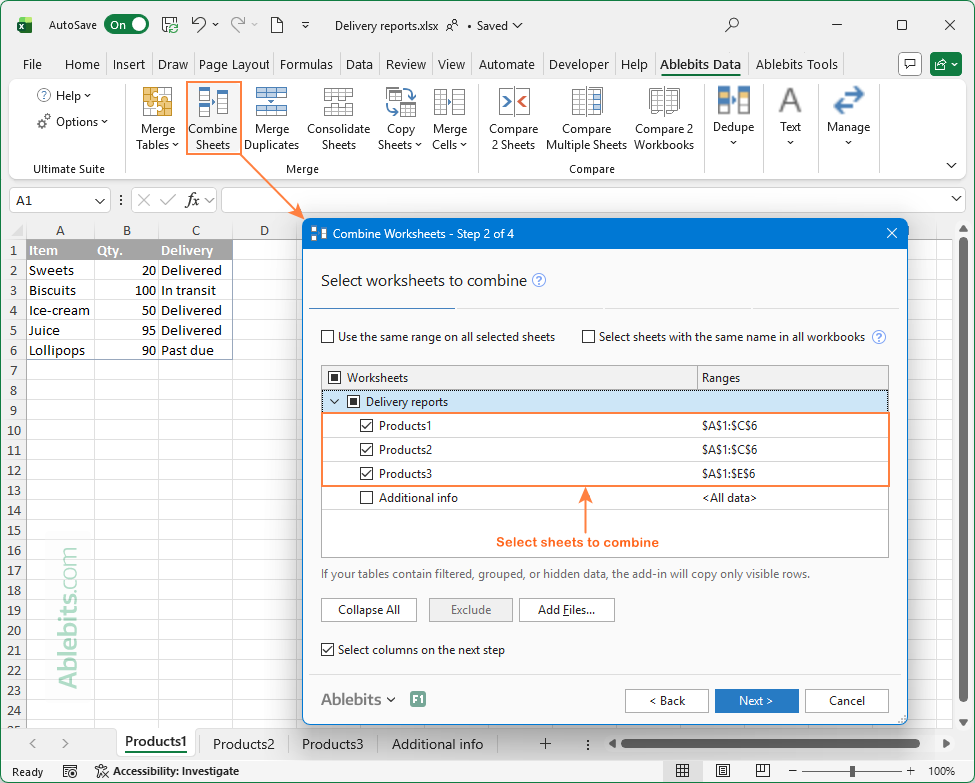
This way, all data will be combined perfectly by column headers:
Combine specific columns from different worksheets
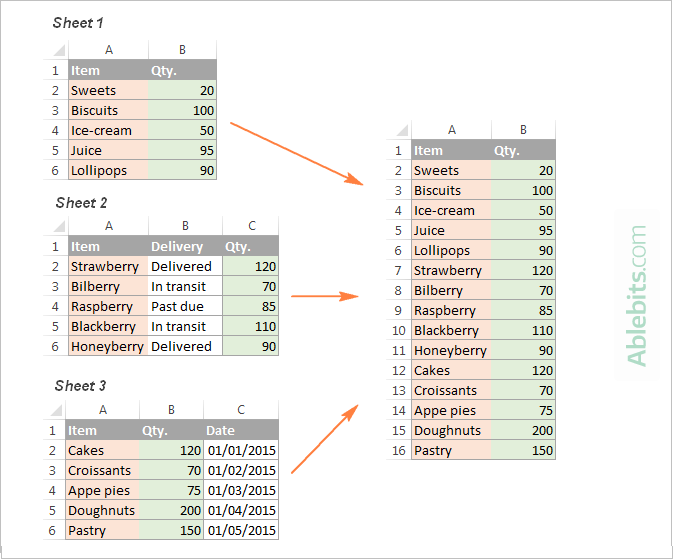
If you're working with large datasets that contain dozens of columns, you may only need the essential ones in your summary. Simply run the Combine Sheets wizard and select the columns you want to keep. It's that easy!
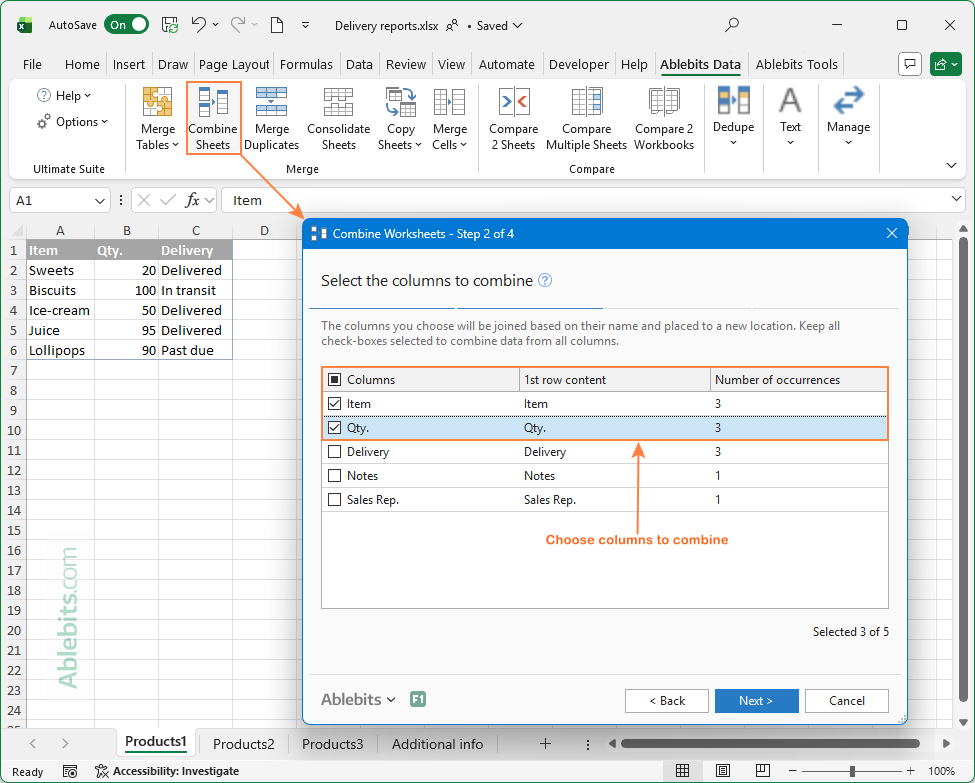
As a result, only the data from the columns that you selected get into the merged sheet:
Merge two Excel sheets into one by the key column
If you are looking for a quick way to match and merge data from two worksheets, Excel's VLOOKUP function is one option. Another is the Merge Tables Wizard, which offers a visual, user-friendly way to compare two Excel spreadsheets by a common column(s) and pull matching data from the lookup table. The screenshot below illustrates what the result can look like.
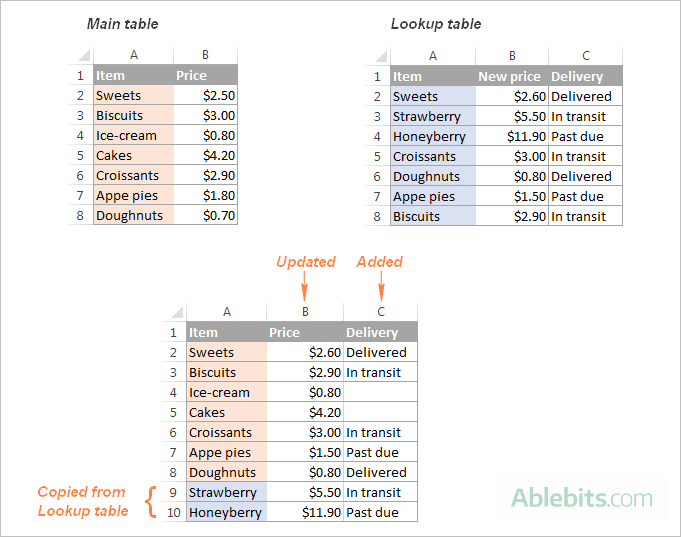
These examples cover only a small part of what our merge tools can do, but there is much more to it! After experimenting a bit, you will see how useful the full toolbox can be. A fully functional trial of the Ultimate Suite is available for download at the end of this post.
Combine data from multiple spreadsheets with Power Query
Power Query is a very powerful technology to combine and refine data in Excel. That said, it's rather complex and requires a long learning curve. The following tutorial explains the common uses in detail: Combine data in Excel with Power Query.
Consolidate data from multiple Excel worksheets into a single sheet
Sometimes you don't need to copy every row from each worksheet – you simply want to summarize the values they contain. That's where data consolidation comes in. Unlike the combining methods described earlier, consolidation produces an aggregated result such as totals, averages, counts, or other summary calculations.
There are two main ways to summarize data in Excel: the built-in Consolidate feature and the Consolidate Sheets tool from Ablebits's Ultimate Suite. Both can pull data from different spreadsheets in one or several workbooks.
That's how you can bring multiple sheets together in Excel. I hope you found this guide useful. Thank you for reading, and I look forward to seeing you here again next week!
Available downloads
Ultimate Suite 14-day fully-functional version (.exe file)
Macros to combine data from multiple sheets (.xlsm file)
 by
by