This is a short step-by-step tutorial for beginners showing how to add VBA code (Visual Basic for Applications code) to your Excel workbook and run this macro to solve your spreadsheet tasks.
Most people like me and you are not real Microsoft Office gurus. So, we may not know all specificities of calling this or that option, and we cannot tell the difference between VBA execution speed in different Excel versions. We use Excel as a tool for processing our applied data.
Suppose you need to change your data in some way. You googled a lot and found a VBA macro that solves your task. However, your knowledge of VBA leaves much to be desired. Feel free to study this step-by-step guide to be able to use the code you found:
Insert VBA code to Excel Workbook
For this example, we are going to use a VBA macro to remove line breaks from the current worksheet.
- Open your workbook in Excel.
- Press Alt + F11 to open Visual Basic Editor (VBE).
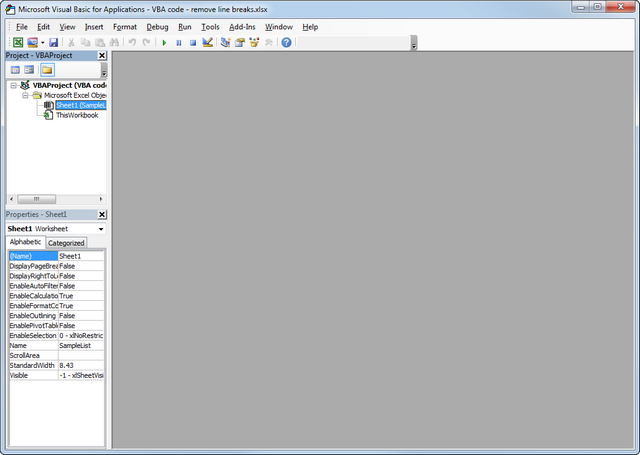
- Right-click on your workbook name in the "Project-VBAProject" pane (at the top left corner of the editor window) and select Insert -> Module from the context menu.
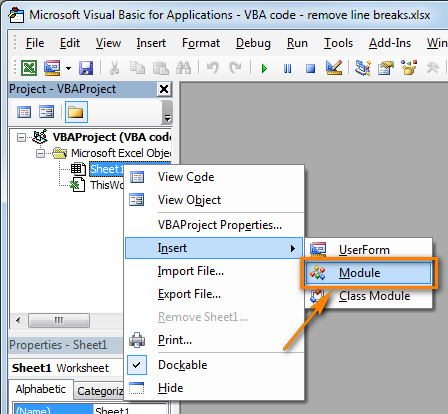
- Copy the VBA code (from a web-page etc.) and paste it to the right pane of the VBA editor ("Module1" window).
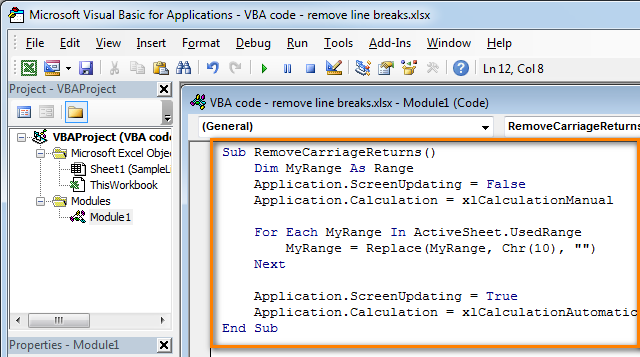
- Tip: Speed up macro execution
If the code of your VBA macro does not contain the following lines in the beginning:
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
Application.Calculation = xlCalculationManualThen add the following lines to get your macro to work faster (see the screenshots above):
- To the very beginning of the code, after all code lines that start with Dim (if there are no "Dim" lines, then add them right after the Sub line):
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
Application.Calculation = xlCalculationManual - To the very of the code, before End Sub:
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
Application.Calculation = xlCalculationAutomatic
These lines, as their names suggest, turn off screen refresh and recalculating the workbook's formulas before running the macro.
After the code is executed, everything is turned back on. As a result, the performance is increased from 10% to 500% (aha, the macro works 5 times faster if it continuously manipulates the cells' contents).
- To the very beginning of the code, after all code lines that start with Dim (if there are no "Dim" lines, then add them right after the Sub line):
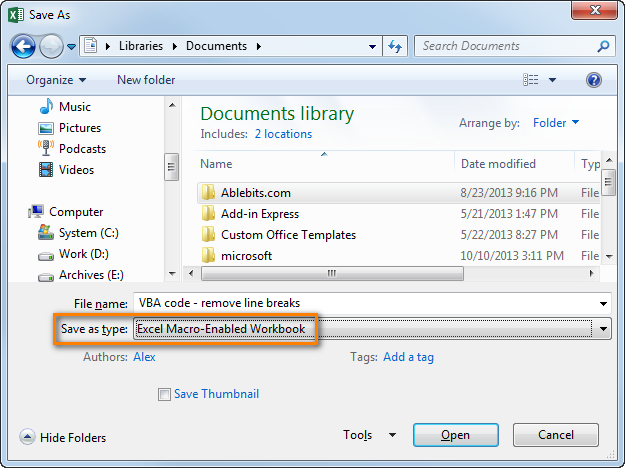
- Save your workbook as "Excel macro-enabled workbook".
Press Crl + S, then click the "No" button in the "The following features cannot be saved in macro-free workbook" warning dialog.

The "Save as" dialog will open. Choose "Excel macro-enabled workbook" from the "Save as type" drop-down list and click the Save button.
- Press Alt + Q to close the Editor window and switch back to your workbook.
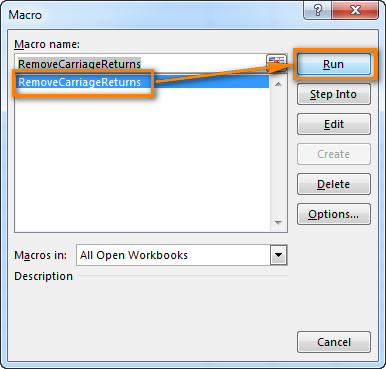
How to run VBA macros in Excel
When you want to run the VBA code that you added as described in the section above: press Alt+F8 to open the "Macro" dialog.
Then select the wanted macro from the "Macro Name" list and click the "Run" button.
 by
by
7 comments
b4.id_code when we enter the id_code Search from the data name & fname displaying this when i enter
b5 name
b6 fname
Hi! To find name and fname by id_code in the data table, don't need VBA code, you can use search formulas, which are discussed in detail in these articles: Excel VLOOKUP tutorial for beginners with formula examples and Excel INDEX MATCH vs. VLOOKUP - formula examples.
I want to use the same VBA code in a few workbooks. Is there a way to enable it across multiple workbooks? Or can I save a VBA as a "favorite" somehow so it is always available?
Hello Roberta!
Here is the article that may be helpful to you: Excel Personal Macro Workbook: how to create, use and share.
Very good try the best
Hi Team,
I would like to inquire about a specific task. In a particular Excel sheet, there exists a dataset. If the data includes the number 4146, it should be transferred to Sheet1. If the data contains the number 4148, it must be moved to Sheet2. Additionally, if the data features the number 4145, it should be relocated to Sheet3.
How to write formula for this??
Thank you in advanc3
Hello Komala!
For each of your three worksheets, you can extract data that matches a specific condition using the FILTER formula.
You can find the examples and detailed instructions here: Excel FILTER function - dynamic filtering with formulas.