In this tutorial, we'll explore the most common reasons why Outlook search fails and walk through practical steps to fix it.
You open Outlook, type in the Search box, and… nothing. No results, even though you're sure the email is there. The issue might come from something as simple as a wrong filter setting or as complex as a broken index. Let's look at what might be going wrong and how to get Outlook search working properly again.
How Outlook search works
To check your emails effectively, it helps to understand how Outlook interprets what you type in the Search box. Below are the key points, with examples for clarity, that explain why you sometimes miss certain messages.
- Prefix matching. Microsoft Outlook uses the so-called prefix matching, which means it looks for words that start with the characters you type. For example, looking for "theo" will find Theodore or Theodora, but not Matheo because "theo" appears in the middle of the word, not at the beginning.
- Case-insensitive search. Outlook doesn't care about capitalization. For instance, "budget", "Budget", or "BUDGET" all return the same results.
- Scans message content and attachments. When you type words in the Search box, Outlook scans both email content and many types of attachments for matches. For example, searching "budget" will return messages containing budget, budgets or budgeting anywhere in the subject line, sender name or email address, To, Cc and Bcc fields, and message body. It will also find an attached file named Budget2025.xlsx, or even the word budget inside a document.
- Searching by email address. If you type an email address into the Search box, Outlook looks for it everywhere, not just in the sender field, but also in the subject line, message body, and even within attachments. To narrow the results to emails from that address, use Outlook search filters like from:ann234@gmail.com or apply the built-in From filter.
- Numbers attached to words. If a number is joined to a word without a space, Outlook treats it as one word. Searching for "365" finds Project 365 (separate word), but not Project365 (joined). To find Project365, you would need to look for that exact combined term.
- Currency and number combinations. If your mailbox is hosted on Exchange Online or Exchange Server 2019, numeric strings starting with a currency must be entered exactly, such as USD20000 or USD 20000. Searching only for 20000 won't match those messages.
- Punctuation is ignored. Outlook ignores punctuation in search queries. For instance, entering "Team Update: Q1." gives the same results as "Team Update Q1" – punctuation marks are simply skipped.
- Deleted items not included. By default, Outlook does not look in the Deleted Items folder. However, you can include this folder in search results if needed by adjusting the settings.
- Search result limits. Outlook shows only the first 1,000 (250 in Outlook 2016 and earlier versions) results for performance reasons. If you don't see what you need, narrow your query with more specific keywords or filters.
- Mixed-language searches. When a search term includes words from different languages, Outlook might show inconsistent results. If possible, search in one language at a time for better accuracy.
- Archive mailboxes. If your organization uses online archive or auto-expanding archiving, emails stored there aren't included in All Mailboxes or All Outlook Items searches in classic Outlook. To check them, select a specific archive folder and set the scope to Current Folder. If it has subfolders, you'll need to search each one separately.
Search in Outlook is not working – how to fix
When search stopped working in Outlook and returns only blank or incomplete results, the cause usually lies in Windows Search Indexing. If indexing is incomplete, paused, or damaged, searches may fail or miss messages. Follow the below steps to check your indexing settings and rebuild them if needed.
Note. This section applies to the classic Outlook application only.
Make sure Outlook is included in Windows Indexing
As the Outlook Find function is powered by the Windows Search indexing service, the first thing to check is that Outlook is included in the indexed locations. To verify this:
- Exit Outlook if it's running.
- Open Control Panel > Indexing Options.
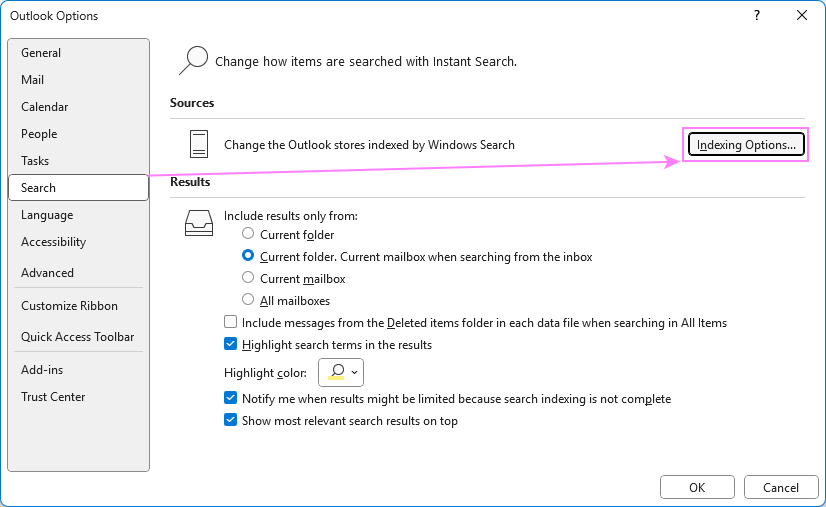
- In the Indexing Options dialog box, verify that Microsoft Outlook appears under Included Locations. If it is missing, click Modify.
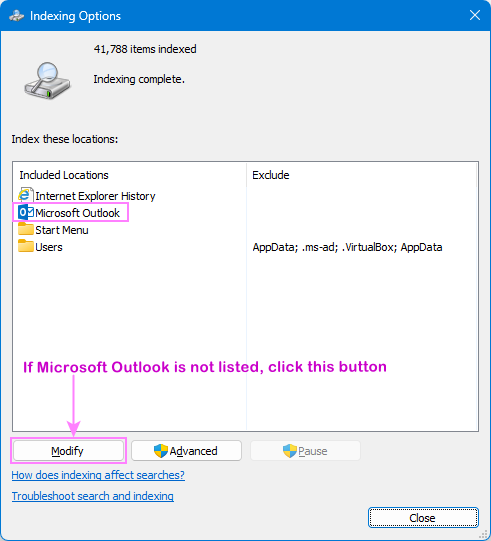
- In the Indexed Locations dialog, select the checkbox next to Microsoft Outlook.
- Click OK to confirm, then close the dialog.
Check indexing status in Outlook
When indexing is incomplete or frozen, Outlook may not have access to all necessary data and return partial or outdated results.
To check the index status:
- In classic Outlook, click inside the Search box to display the Search tab.
- On the Search tab, in the Options group, click Search Tools > Indexing Status.
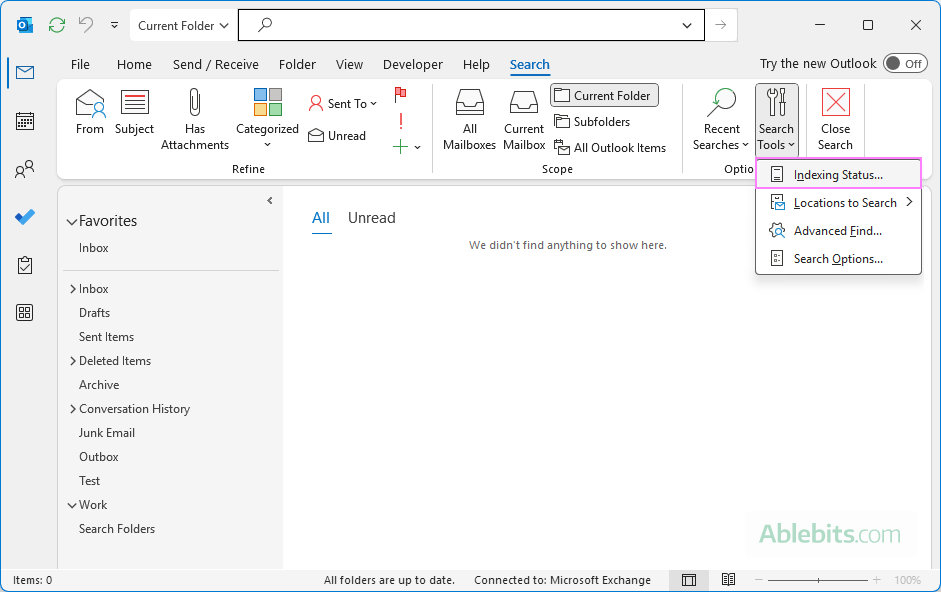
- Review the displayed message:
- If it says Outlook has finished indexing all of your items, you are good to go – close the dialog.
- If it shows X items remaining to be indexed, leave Outlook open for a while to let the process finish, and then check again.
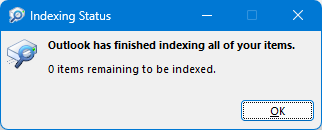
If the number doesn't decrease after several minutes, indexing is likely to be paused or stuck. In this case, move on to rebuilding the index.
Rebuild Outlook index
The search index works like a catalog, storing key terms from all your messages, calendar entries, and contacts so Outlook can locate them quickly. If this catalog becomes corrupted, rebuilding it forces Windows to recreate a fresh, accurate index.
To rebuild the index:
- Close the classic Outlook application.
- Open Control Panel and click Indexing Options.
- In the window that opens, click Advanced.
- Under Troubleshooting, select Rebuild.
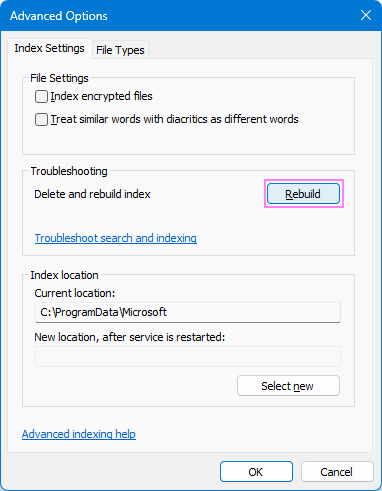
- Confirm with OK, and then close the dialog box.
- Once the new index is created, restart Outlook.
Note. Rebuilding can take several hours, depending on the size of your mailbox. You can continue using Outlook during the process, but search results will update gradually as indexing completes.
Configure Outlook indexing options correctly
If Outlook search still doesn't return complete results, it's worth checking that indexing options are properly configured for MSG files – the file type Outlook uses for email messages.
- Close Outlook if it's currently open.
- Go to Control Panel > Indexing Options.
- In the Indexing Options dialog box, click Advanced.
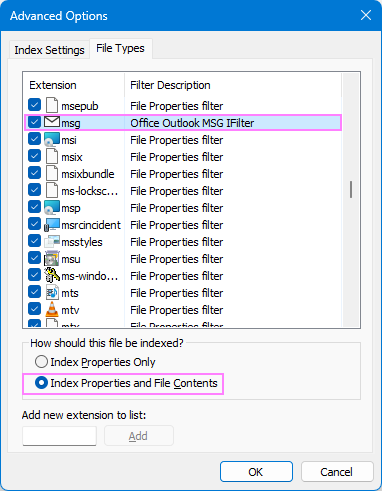
- Go to the File Types tab.
- In the Extension column, scroll down to locate msg and select it.
- Under How should this file be indexed, make sure Index Properties and File Contents is selected.
- Check the Filter Description column. It should display Office Outlook MSG IFilter. If it doesn't, the Windows Search service may not be functioning correctly, or Outlook didn't install the filters properly. In that case, you may need to reinstall Outlook or contact your IT department or Microsoft Support for assistance.
- Click OK, and then click Close.
Check that all Outlook data files are included in search
If you have multiple accounts in your Outlook, make sure all are part of the search index. If some mailboxes aren't indexed, their contents won't appear in search results.
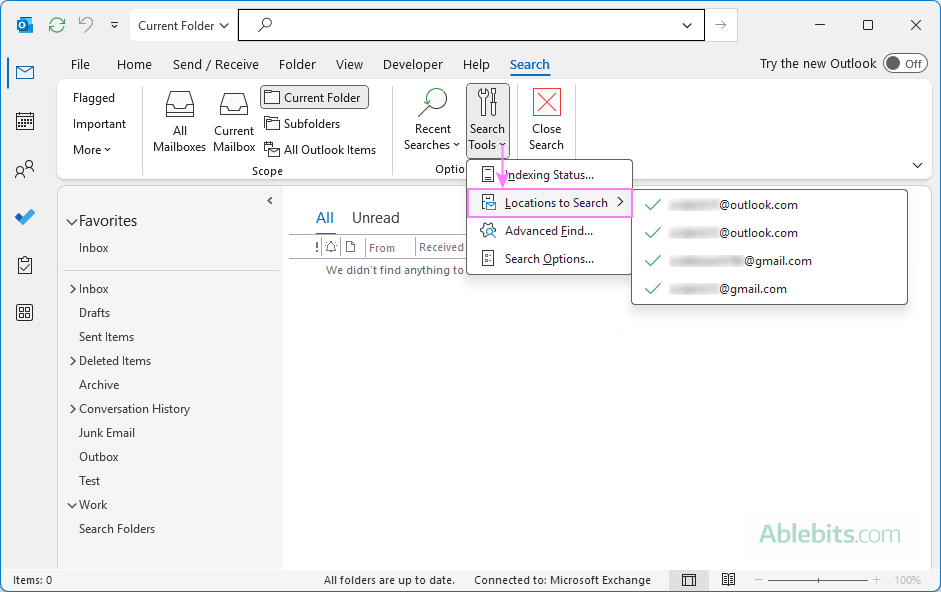
- In classic Outlook, click inside the Search box.
- On the ribbon, go to the Search tab, and click Search Tools > Locations to Search.
- Ensure all listed accounts are selected.
Confirm Windows Search Service is running
If the Windows Search Service is disabled, Outlook can't use indexing at all.
To verify and start the service:
- Open the Windows Start menu, type services.msc in the Search box and press Enter.
- In the Services window, find Windows Search in the Name column and double-click it.
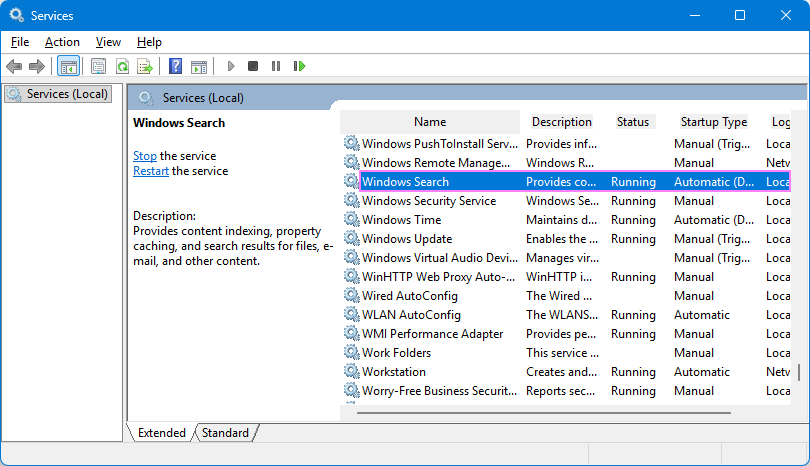
- Set the Startup type to Automatic (Delayed Start) if it isn't already.
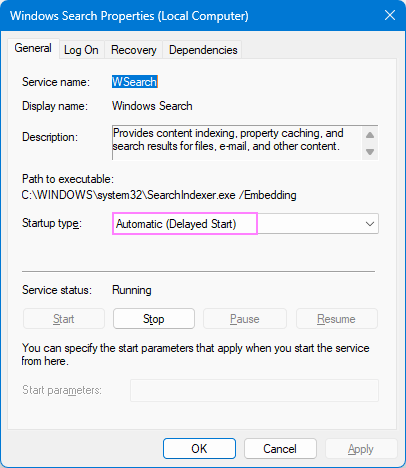
- If the Service status isn't Running, click Start.
- Click OK to apply changes.
Verify Group Policy isn't blocking Outlook indexing
If you are using the Pro edition of Windows 10 or Windows 11, indexing behavior can be managed through the Local Group Policy Editor. Certain policies might block Outlook or specific folders from being indexed, which can prevent search from working correctly.
To verify that indexing isn't restricted:
- Press Win + R to open the Run dialog.
- Type gpedit.msc and press Enter. This will open the Local Group Policy Editor.
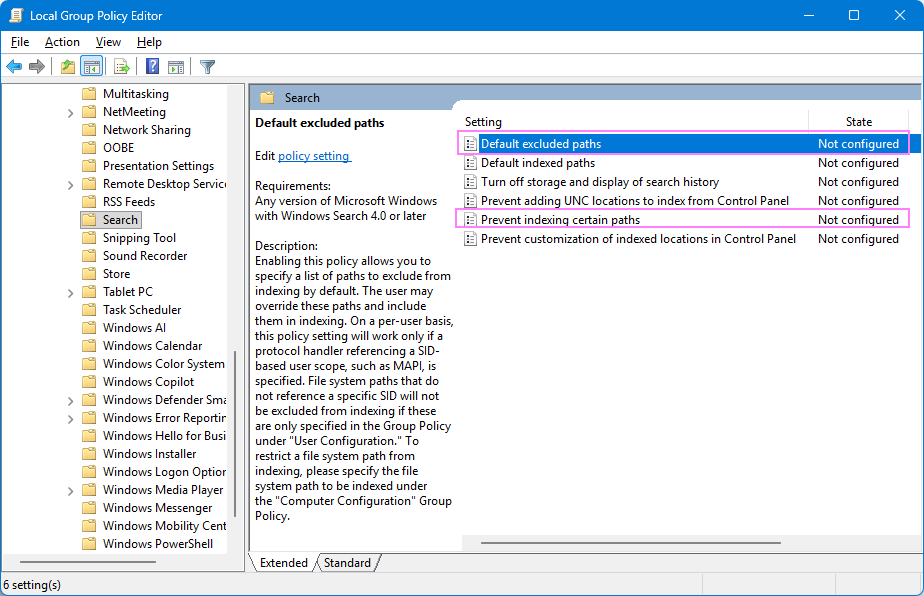
- In the left pane, navigate to User Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Search.
- In the right pane, locate the Default excluded paths and Prevent indexing certain paths settings.
- Check their current State:
- If both are set to Not configured, indexing is allowed – no changes are needed.
- If either setting is configured differently, double-click it, select Not configured, and click OK.
Once done, close the Group Policy Editor and restart Outlook.
Run Windows Search troubleshooter
If you're using Windows 10 or an earlier version, you can use the built-in Search and Indexing Troubleshooter to automatically detect and fix common problems with Windows Search.
To run the troubleshooter:
- Press Win + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type the following command and press Enter:
msdt.exe -ep WindowsHelp id SearchDiagnostic - The Search and Indexing Troubleshooter will open. Click Next and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the process.
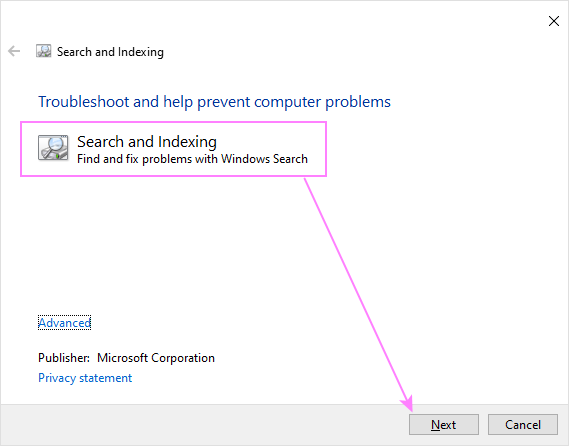
Alternatively, you can launch it through Windows Settings. The exact steps vary depending on your Windows version. On Windows 10, go to Settings > Update & Security > Troubleshoot > Additional troubleshooters > Search and Indexing.
Note. Microsoft is retiring some built-in troubleshooters and the Microsoft Support Diagnostic Tool (MSDT) that powers them. On Windows 11, version 23H2 and later, the Search and Indexing troubleshooter is no longer available.
After completing these steps, give Outlook some time to rebuild its index. Once complete, try your search again – it should start showing accurate results.
Outlook Find returns incomplete results
If Outlook omits some items you expect to see, the issue may be related to how the search scope or filters are set. Try the steps below to refine your searches.
Adjust the search scope
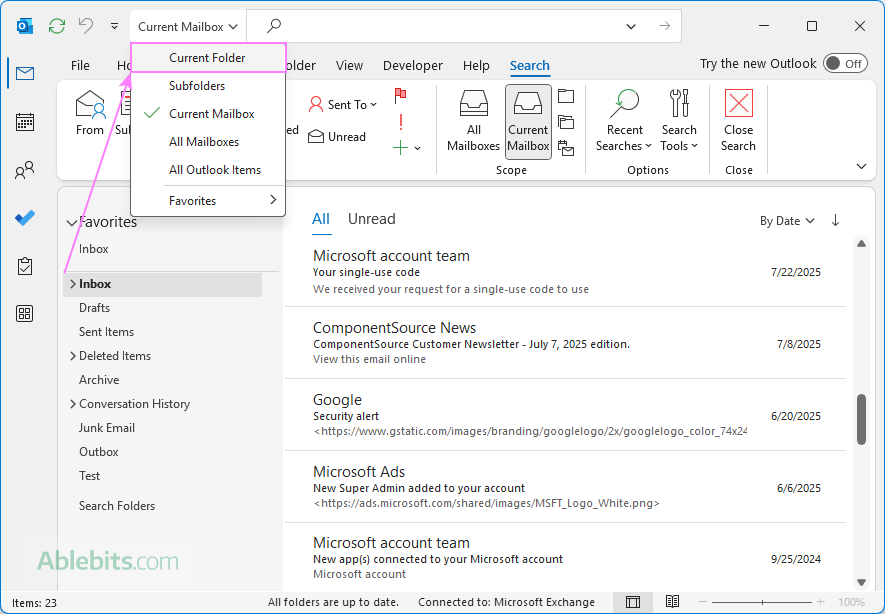
When searching in Outlook from the Inbox folder, it checks the entire mailbox by default. To limit the search to only Inbox, adjust the scope:
- On the Search tab, in the Scope group, select Current Folder, or
- Choose Current Folder from the dropdown menu to the left of the Search box.
For more information, see How to search emails in Outlook.
Use search filters to refine results
If Outlook results include many irrelevant messages, filters can help narrow things down. Use inbuilt filters (such as From, Subject, Has Attachments, etc.) or custom text filters to target specific items.
Include Deleted items folder in search
If you still can't find certain messages, they may have been deleted earlier. You can have Outlook check the Deleted Items folder as well by adjusting this setting:
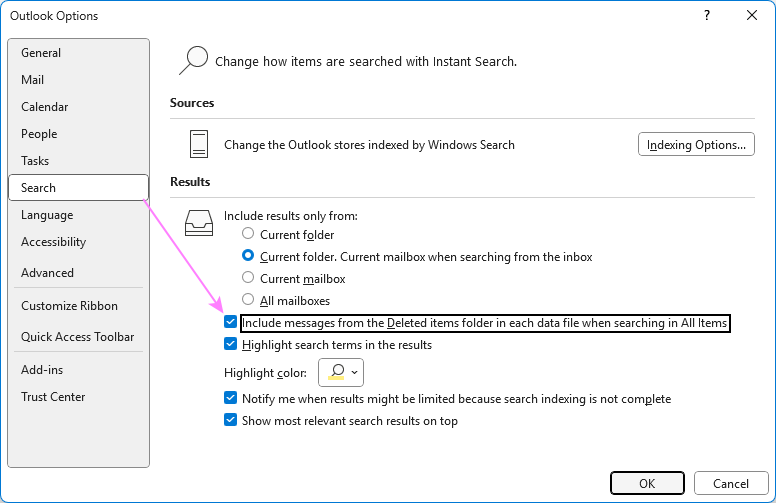
- In classic Outlook, go to File > Options > Search.
- Under Results, select the checkbox named Include messages from the Deleted Items folder in each data file when searching in All Items, and click OK.
- Restart Outlook for the change to take effect.
Download past emails
Outlook can only scan emails that are cached locally on your computer. For Microsoft 365, Outlook.com, and other Exchange accounts (both online and on-premises), emails are stored on the server and synced to a local .ost file. By default, Outlook downloads and indexes only 1 year of emails. Messages older than that remain on the server and won't appear in search results.
To download and make all past emails searchable:
- In classic Outlook, go to File > Account Settings > Account Settings.
- On the Email tab, select the target account and click Change.
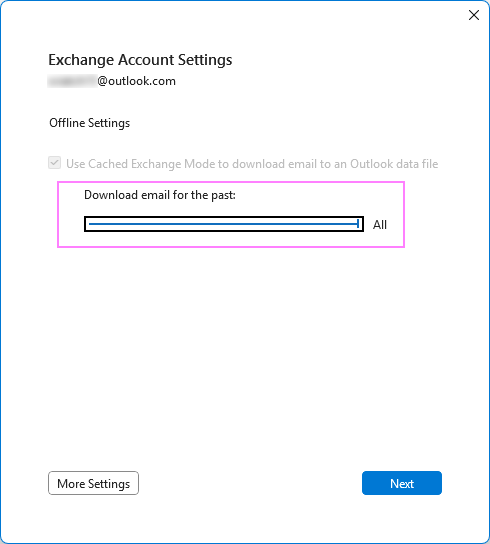
- Make sure the Use Cached Exchange Mode to download emails box is selected.
- Under Download email for the past, move the slider to the desired time range or drag it all the way to the right to select All.
- Click Next, then Done.
- Restart Outlook to begin syncing the additional emails.
Search not working in new Outlook
Unlike the classic desktop application, the new Outlook doesn't depend on Windows indexing. Instead, it uses Microsoft's cloud-based search, which means issues with local indexing don't apply here.
If the new Outlook search doesn't work properly, adjusting a couple of key settings may resolve the issue.
Download older emails
By default, the new Outlook downloads only emails from the last 30 days for offline use. Expanding the sync range allows it to include older messages in searches.
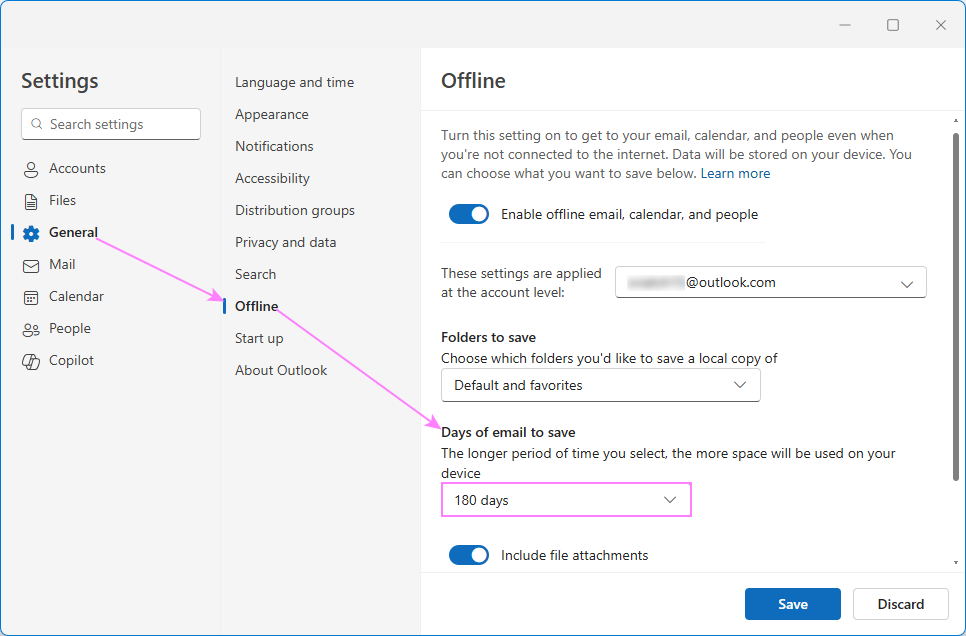
- Go to Settings > General > Offline.
- Under Days of email to save, select the desired time range from the dropdown menu, a maximum of 180 days.
- Click Save.
Notes:
- The sync range is applied at the account level, so you'll need to adjust it separately for each email account you use in the new Outlook.
- The longer period you set, the more storage space Outlook will use on your device.
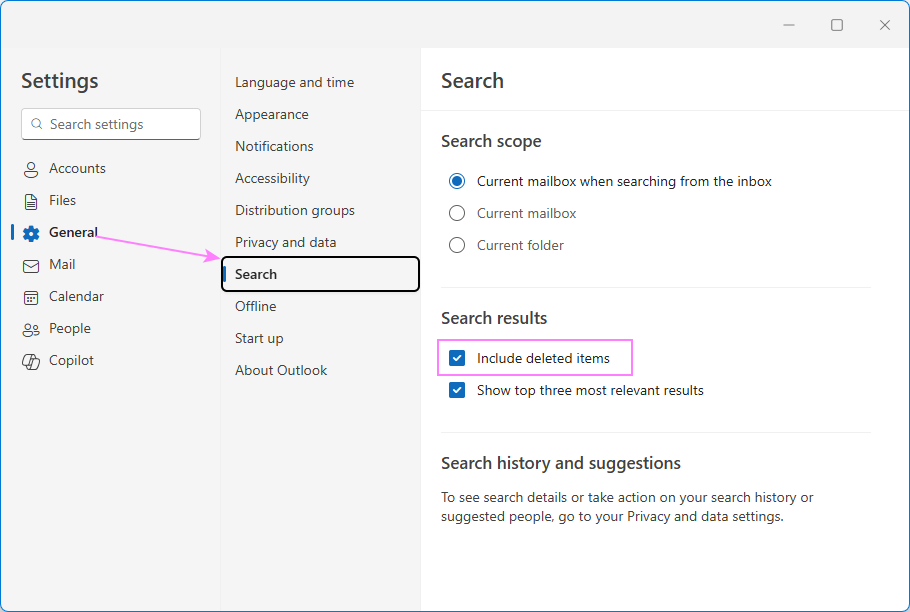
Adjust new Outlook search settings
You can also review Outlook search preferences to include deleted items and set your preferred scope.
- Go to Settings > General > Search.
- Include Deleted Items folder. If you think missing emails may have been deleted, make sure Include deleted items is checked under Search results.
- Adjust default scope. Choose whether Outlook scans the Current Mailbox or Current Folder by default.
- Click Save.
Notes:
- Multi-account search is not currently supported. You'll need to select each account individually and search within All Folders.
- Online archives are automatically included in Current Mailbox results, unlike in classic Outlook.
General troubleshooting to fix Outlook search issues
If the specific fixes in the first part of this tutorial didn't resolve your Outlook search problem, try the general troubleshooting methods below. These solutions address common causes of Outlook errors and can often restore normal functionality.
Update Outlook and Windows
Outlook search problems can sometimes occur due to outdated components or compatibility issues between Outlook and Windows. Keeping both applications up to date ensures you have the latest performance improvements and bug fixes.
For detailed steps, see How to update Outlook classic and new.
Repair Your Outlook Data Files
Corrupted Outlook data files (.pst or .ost) can disrupt how Outlook locates messages and lead to other unexpected issues. Repairing these files gives Outlook a fresh index to work from, which usually resolves the problem.
For instructions, see How to repair Outlook Data Files.
Check for conflicts with third-party search tools
If you use any third-party utilities, they may conflict with Outlook's built-in search function. These tools often interfere with Windows indexing, which can lead to incomplete or missing results.
To check if this might be the cause, temporarily disable any non-Microsoft add-ins:
- In Outlook, go to File > Options > Add-ins.
- At the bottom, select COM Add-ins from the Manage dropdown and click Go.
- Clear the checkboxes next to any non-Microsoft add-ins, then click OK.
Restart Outlook and test search again. If it starts working correctly, the issue was likely caused by one of the disabled tools.
Test search in new Outlook profile
Sometimes, issues stem from a damaged or misconfigured Outlook profile. You can test this by creating a new profile and checking if Outlook's Find works there. If it works correctly in the new profile, your old profile may be the problem. In that case, you can:
- Make the new profile your default, and
- Transfer your data and settings from the old profile to the new one.
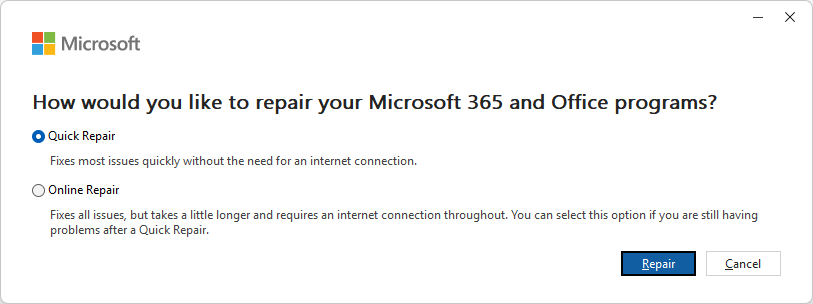
Repair or reinstall Office
If none of the above methods help, the Outlook installation itself may be damaged. Repairing Office can restore missing or corrupted program files.
- Navigate to Control Panel > Programs and Features.
- Select Microsoft Office or Microsoft 365 Apps, then choose Change > Quick Repair.
- If the issue persists, try the Online Repair option for a deeper fix.
For more details, see How to repair Outlook 365 – 2013 app.
By now, you've explored every major cause of Outlook search issues, from simple settings checks to deeper repairs. Once all the troubleshooting steps are complete, restart Outlook and check if it finds your emails accurately again. If it still doesn't return results as expected, it may be time to contact your IT team or Microsoft Support for personalized help.
 by
by